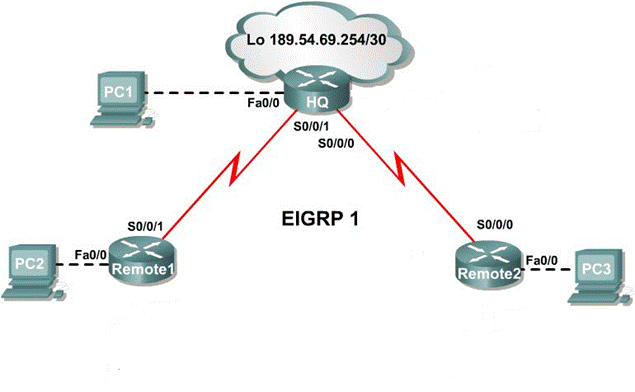
Case 1: Create an Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Use the 147.144.0.0/16 address to create an addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. Begin the address assignments with the 147.144.64.0 address. Start with the largest subnet and assign address blocks in decreasing order of size, without skipping any addresses.
Document all subnet addresses in Table 1.
Table 1
|
Interface |
Number of Hosts |
Subnet |
Subnet Mask |
|
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
14000 |
147.144.64.0/18 |
255.255.192.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
147.144.193.0/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
147.144.193.4/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
8191 |
147.144.128.0/18 |
255.255.192.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
147.144.193.0/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
127 |
147.144.192.0/24 |
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
147.144.193.4/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
Step 2: Document router interface
and PC addresses in Table 2.
Assign the last usable IP address of each subnet to each PC. Assign the first usable IP address of each
subnet to each default gateway.
Table 2
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
147.144.64.1 |
255.255.192.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
147.144.193.1 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
147.144.193.5 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Lo0 |
189.54.69.254 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
147.144.128.1 |
255.255.192.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
147.144.193.2 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
147.144.192.1 |
255.255.255.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
147.144.193.6 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
PC1 |
Ethernet |
147.144.127.254 |
255.255.192.0 |
147.144.64.1 |
|
PC2 |
Ethernet |
147.144.191.254 |
255.255.192.0 |
147.144.128.1 |
|
PC3 |
Ethernet |
147.144.192.254 |
255.255.255.0 |
147.144.192.1 |
Case 2: Create an Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Use the 10.17.0.0/16 address to create an addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. Begin the address assignments with the 10.17.128.0 address. Start with the largest subnet and assign address blocks in decreasing order of size, without skipping any addresses.
Document all subnet addresses in Table 1.
Table 1
|
Device |
Interface |
Number of Hosts |
Subnet |
Subnet Mask |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
3600 |
10.17.128.0/20 |
255.255.240.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
10.17.146.64/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
10.17.146.68/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
256 |
10.17.144.0/23 |
255.255.254.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
10.17.146.64/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
43 |
10.17.146.0/26 |
255.255.255.192 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
10.17.146.68/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
Step 2: Document router interface
and PC addresses in Table 2.
Assign the last usable IP address of each subnet to each PC. Assign the first usable IP address of each
subnet to each default gateway.
Table 2
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
10.17.128.1 |
255.255.240.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
10.17.146.65 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
10.17.146.69 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Lo0 |
189.54.69.254 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
10.17.144.1 |
255.255.254.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
10.17.146.66 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
10.17.146.1 |
255.255.255.192 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
10.17.146.70 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
PC1 |
Ethernet |
10.17.143.254 |
255.255.240.0 |
10.17.128.1 |
|
PC2 |
Ethernet |
10.17.145.254 |
255.255.254.0 |
10.17.144.1 |
|
PC3 |
Ethernet |
10.17.146.62 |
255.255.255.192 |
10.17.146.1 |
Case 3: Create an Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Use the 192.99.0.0/16 address to create an addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. Begin the address assignments with the 192.99.0.0 address. Start with the largest subnet and assign address blocks in decreasing order of size, without skipping any addresses.
Document all subnet addresses in Table 1.
Table 1
|
Device |
Interface |
Number of Hosts |
Subnet |
Subnet Mask |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
1100 |
192.99.128.0/21 |
255.255.248.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
192.99.136.32/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
192.99.136.36/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
15 |
192.99.136.0/27 |
255.255.255.224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
192.99.136.32/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
30000 |
192.99.0.0/17 |
255.255.128.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
192.99.136.36/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
Step 2: Document router interface
and PC addresses in Table 2.
Assign the last usable IP address of each subnet to each PC. Assign the first usable IP address of each
subnet to each default gateway.
Table 2
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
192.99.128.1 |
255.255.248.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
192.99.136.33 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
192.99.136.37 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Lo0 |
189.54.69.254 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
192.99.136.1 |
255.255.255.224 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
192.99.136.34 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
192.99.0.1 |
255.255.128.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
192.99.136.38 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
PC1 |
Ethernet |
192.99.135.254 |
255.255.248.0 |
192.99.128.1 |
|
PC2 |
Ethernet |
192.99.136.30 |
255.255.255.224 |
192.99.136.1 |
|
PC3 |
Ethernet |
192.99.127.254 |
255.255.128.0 |
192.99.0.1 |
Case 4: Create an Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Use the 223.255.0/16 address to create an addressing scheme to accommodate all hosts on the network. Begin the address assignments with the 223.255.192.0 address. Start with the largest subnet and assign address blocks in decreasing order of size, without skipping any addresses.
Document all subnet addresses in Table 1.
Table 1
|
Device |
Interface |
Number of Hosts |
Subnet |
Subnet Mask |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
4191 |
223.255.192.0/19 |
255.255.224.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
223.255.240.32/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
223.255.240.36/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
2047 |
223.255.224.0/20 |
255.255.240.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
2 |
223.255.240.32/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
15 |
223.255.240.0/27 |
255.255.255.224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
2 |
223.255.240.36/30 |
255.255.255.252 |
Step 2: Document router interface
and PC addresses in Table 2.
Assign the last usable IP address of each subnet to each PC. Assign the first usable IP address of each
subnet to each default gateway.
Table 2
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|
HQ |
Fa0/0 |
223.255.192.1 |
255.255.224.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
223.255.240.33 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
S0/0/0 |
223.255.240.37 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Lo0 |
189.54.69.254 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote1 |
Fa0/0 |
223.255.224.1 |
255.255.240.0 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/1 |
223.255.240.34 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
Remote2 |
Fa0/0 |
223.255.240.1 |
255.255.255.224 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0/0/0 |
223.255.240.38 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
|
|
PC1 |
Ethernet |
223.255.223.254 |
255.255.224.0 |
223.255.192.1 |
|
PC2 |
Ethernet |
223.255.239.254 |
255.255.240.0 |
223.255.224.1 |
|
PC3 |
Ethernet |
223.255.240.30 |
255.255.255.224 |
223.255.240.1 |
Last revised 12-7-10