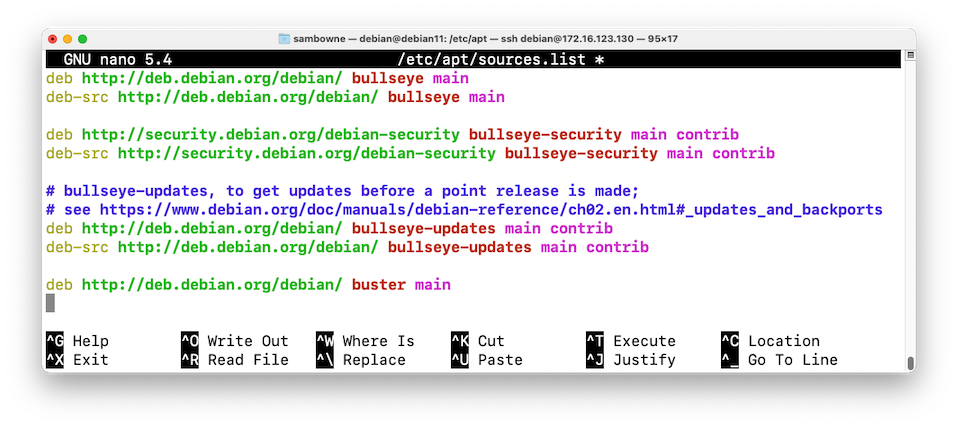
On your Debian 11 server, in an SSH shell, execute this command:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ buster main

Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
Execute these commands, one at a time, approving the changes:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install open-cobol
sudo apt --fix-broken install
sudo apt install open-cobol
nano hello.cbl
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. HELLO-WORLD.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
DISPLAY 'Hello world!'.
STOP RUN.
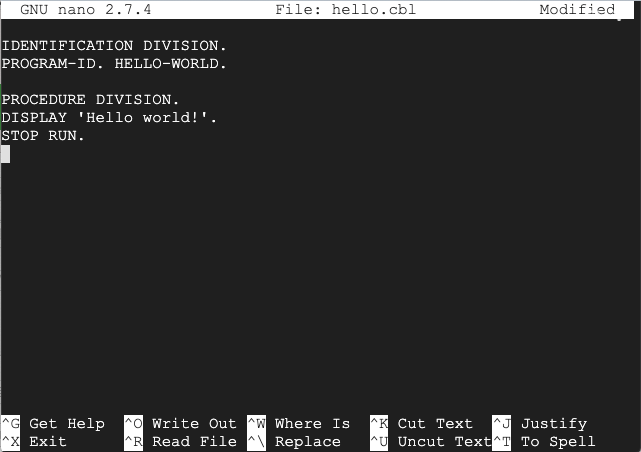
Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
Execute these commands to compile the code and run it:
cobc -free -x -o hello hello.cbl
./hello
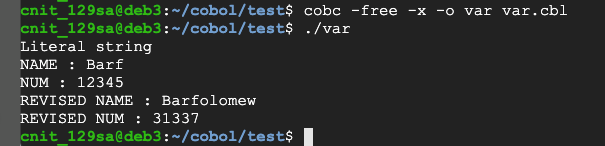
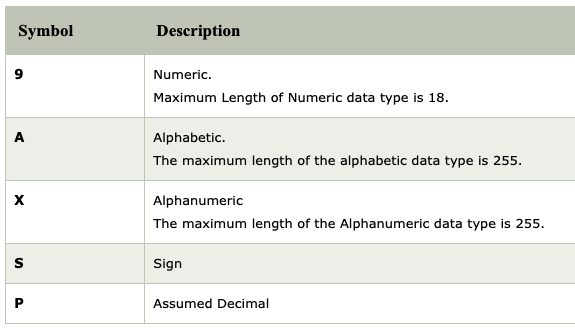
Flag CBL 1.1: File Type (5 pts)
Execute this command to see the file type of the executable:The flag is the last word in the response, covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
nano var.cbl
This program defines two variables, a string called NAME and a number called NUM. It also modifies them using the MOVE command.
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. VAR.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NAME PIC A(20) VALUE 'Barf'.
01 NUM PIC 9(5) VALUE 12345.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A-PARA.
DISPLAY 'Literal string'.
DISPLAY "NAME : "NAME.
DISPLAY "NUM : "NUM.
MOVE 'Barfolomew' TO NAME.
MOVE 31337 TO NUM.
DISPLAY "REVISED NAME : "NAME.
DISPLAY "REVISED NUM : "NUM.
STOP RUN.
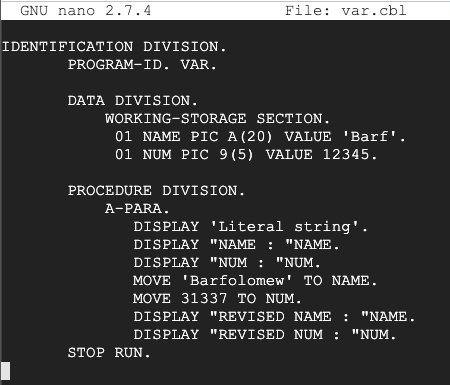
Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
Execute these commands to compile the code and run it:
cobc -free -x -o var var.cbl
./var
Flag CBL 1.2: COMPUTE (10 pts)
Modify your program by adding the three lines outlined in green in the image below.
Compile and run the program to see the flag, which is covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
http://ad.samsclass.info/COBOL/
A very simple page appears, as shown below.
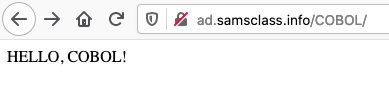
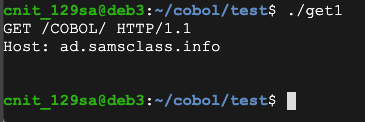
Create a file named get1.cbl that constructs the GET request to load that page, as shown below.
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. GET1.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 GETLINE PIC A(20).
01 HOSTLINE PIC A(24).
01 CR PIC X VALUE X'0A'.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A-PARA.
MOVE "GET /COBOL/ HTTP/1.1" TO GETLINE.
MOVE "Host: ad.samsclass.info" TO HOSTLINE.
DISPLAY GETLINE.
DISPLAY HOSTLINE.
DISPLAY CR.
STOP RUN.
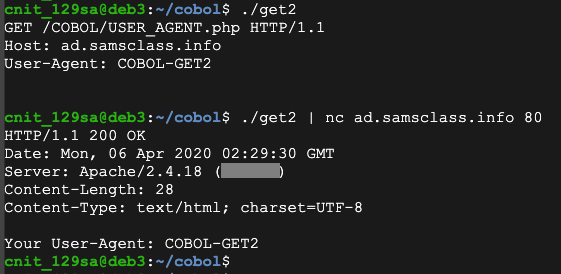
Flag CBL 1.3: Server Version (10 pts)
Execute these commands to send that request to the server:The flag is covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
Note that the GET line has changed also.
Send it to the server and the server will echo it back to you, as shown below.
Flag CBL 1.4: FLAG_ME (15 pts)
Send a request with a User-Agent of FLAG_ME to get the next flag, covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. LOOP.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NUM PIC 9(1) VALUE 0.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A-PARA.
PERFORM B-PARA WITH TEST AFTER UNTIL NUM>3.
STOP RUN.
B-PARA.
DISPLAY 'NUM : 'NUM.
ADD 1 TO NUM.
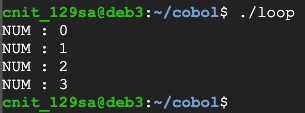
Flag CBL 1.5: Total (10 pts)
Make a loop that totals the numbers from 10 through 49.The flag is that total, covered by a green rectangle in the images below.
...
Flag CBL 1.6: Fib(100) (15 pts)
Create a COBOL program to calculate Fibonacci numbers, as shown below.Find the 100th value. The flag is that value, covered by a green rectangle in the images below.
...
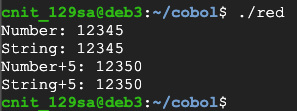
Create a file named red.cbl as shown below.
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. RED.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 A PIC 9(5) VALUE 12345.
01 B REDEFINES A PIC A(5).
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A-PARA.
DISPLAY "Number: "A.
DISPLAY "String: "B.
ADD 5 TO A.
DISPLAY "Number+5: "A.
DISPLAY "String+5: "B.
STOP RUN.
Flag CBL 1.7: Numerical User-Agent (20 pts)
Make a loop that sends user agents from 0 through 9 to the server you used in Flag CBL 1.4.One of the responses shows a flag, covered by a green rectangle in the images below.
Hint: to concatenate strings, use STRING.
...
...
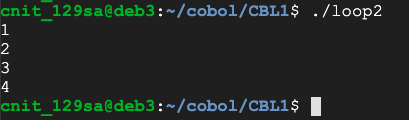
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. LOOP2.
DATA DIVISION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NUM PIC 9(1).
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
A-PARA.
PERFORM VARYING NUM FROM 1 BY 1 UNTIL NUM>4
DISPLAY NUM
END-PERFORM.
STOP RUN.
Flag CBL 1.8: Pythagoras (15 pts)
Find integers A, B, and C that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem:A*A + B*B = C*CAll three numbers should be between 1 and 100, and they should be in ascending order:A < B < CThe image below shows the first few results.The flag is the last set of results in the format shown below: three two-digit numbers with spaces between them.
Flag CBL 1.9: Rail Fence Cipher (15 pts)
Implement the Rail fence cipher, as shown below.
Decode this text to see the flag:
T_EEASIAHSTM_H_LGI_ALODIITF_RR
Flag CBL 1.10: Rail 5 (15 pts)
Implement the rail cipher with five rails, as shown below.
Decode this text to see the flag:
RUFEAON_LRRLRDEAOAL__HGMISYT_L
Flag CBL 1.11: Viginere Cipher With the Keyword (15 pts)
Implement the Viginere cipher, as shown below.
Decode this text with the keyword ORANGE to see the flag:
HYIF_XWDE_LPOX_VY_DFLLGPDYA
Flag CBL 1.12: Viginere Cipher Without the Keyword (15 pts)
Decode this text. The keyword is three letters long. The plaintext includes the word "FLAG".YVB_TIFU_NG_XSXWQENBD
Posted 4-5-2020 by Sam Bowne
CBL 1.8 added 4-9-2020
CBL 1.9 - 1.12 added 4-10-2020
Updated for Debian 11 6-24-22